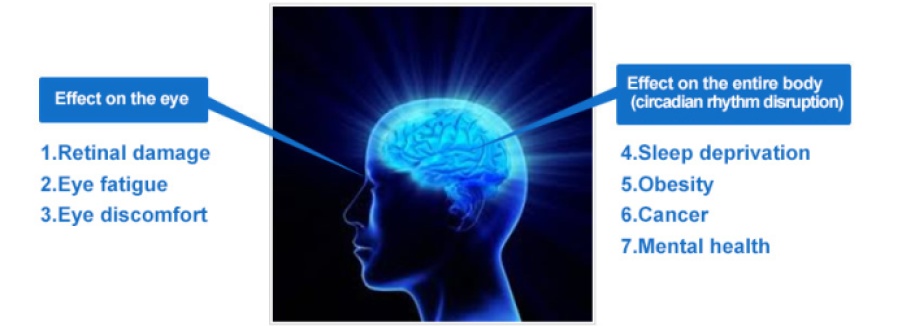
But bad lighting is associated with a range of ill health effects both physical and mental such as eye strain headaches fatigue and also stress and anxiety in more high pressured work.
Effects of office lighting on mood and cognitive performance.
However an interaction between gender and color temperature on mood showed that 3000k more reddish and 4000k more bluish office lighting may communicate different affective loadings or meanings to each gender.
Other studies found that lighting can affect appetite.
However an interaction between gender and color temperature on mood showed that 3000k more reddish.
The results showed no significant effect of the lighting on the performance of cognitive tasks.
As a matter of fact it has been documented that insufficient lighting can contribute to depression and deficiency in vitamin d.
Yet these investigations did not render a conclusive or consistent finding on the relative contribution of illuminance and cct on various cognitive domains.
Research has explored acute effects of light level and correlated color temperature cct of indoor lighting on subjective measures of alertness and task performance during daytime.
Thus subjects mood valences and their cognitive performances varied significantly with the genders emotionally different reactions to the indoor lighting.
In addition a gender effect in the performance appraisal task was examined both as a between and within subject factor.
The results showed no significant effect of the lighting on the performance of cognitive tasks.
Proper lighting on the other hand has been known to improve mood and energy levels.
The same applies to office workers who suffer from the same symptoms in the long term.
This suggests in practice that the criteria for good indoor lighting may be revised taking into account females and males emotional and cognitive responses as well.
Exposure to dynamic light during office hours is essential for sustainable employability.